
He had been studying for his astronomy final when the doorbell rang.The past perfect continuous tense describes an ongoing action that-like the past perfect-was performed in relation to another event that occurs closer to the present. It is formed by combining had been with the present participle of the verb. One action occurred ( had recommended) before the other ( bought). The girl bought (simple past) what the teacher had recommended (past perfect tense). The girl bought the telescope her teacher had recommended to her.It is formed by combining had and the past participle of the verb. The past perfect tense, also called the pluperfect tense, describes a past event in relation to another event that occurs closer to the present. They build upon simple tenses by combining a verb with has, have, or had. The perfect tenses involve more complex time relationships. were so you won’t have any mistakes again. In this example, the verb tense says that the planet began moving sometime in the past and continued to do so for a period of time (in the past).Įstablish the different times to use was vs. The planet was moving along an elliptical orbit.It is formed by combining the past tense verb to be (which must be correctly conjugated to agree with the subject) and the present participle of a verb (ending in – ing): The past continuous tense describes an ongoing activity that occurred in the past. In this example, the verb tense indicates that the astronomer Galileo completely finished the act of observing the stars at some point in the past. Simple past is usually used to write about historical events, like so: For example, go becomes went, and think becomes thought. However, many irregular verbs have unique past tense forms. Most verbs can be made past tense by adding -ed, – d, or sometimes the variant – t at the end of a present tense verb, as in liked and watched. The simple past tense describes events that have already happened and are completely finished. Past perfect continuous: describes an event that began in the past, continued for a length of time, and was in progress when another past event happened.

Past perfect: describes a past event that occurred before another past event.Past continuous: describes events that began in the past, continued for a length of time, and ended in the past.
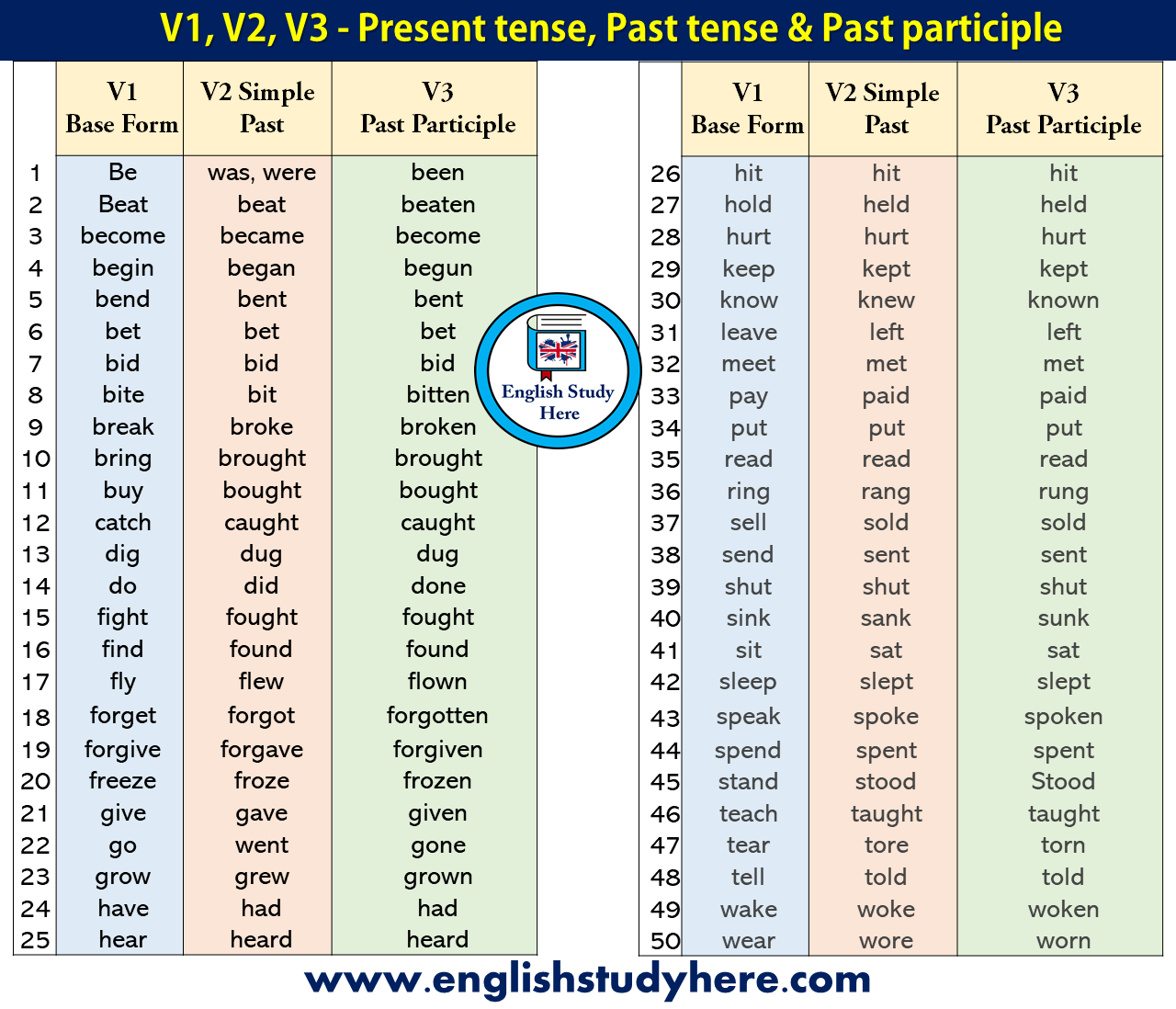
Simple past: describes events that began and ended in the past.There are four variations of past tenses: The past tenses use verbs to say that something happened in the past, meaning any time before this moment right now. The simple tenses ( past, present, and future) are the most basic forms, but there are 12 major verb tenses in English in all. We’ll review the tenses here. A separate word (or particle) is combined with the verb to explain when it occurred. In Chinese languages, for example, a verb doesn’t change its spelling depending on the tense. ( Walk becomes walks and walked.) In some cases, an auxiliary verb (also known as a helping verb, like will or need) is required as well. Interestingly, not all languages treat verb tenses the same way. In English, the ending on a verb communicates what tense it’s in. The verb walks communicates not only how many people completed the action (it’s singular), but also when it occurred. Generally speaking, verb tenses identify the time period when an action occurs. In the sentences the boy walks and the girl ran, the words walks and ran are the verbs.ĭid you also recognize that walks is in the present tense, or that ran is in the past tense? Whether you did or didn’t, we’re here to review verb tenses with you and also astound you with the fact that there are 12-count them, 12-verb tenses in all!

If you’re familiar with basic English grammar, we bet you can describe a verb and perhaps name a tense or two.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
